Chameleónovité in Modern Zoological Studies
Chameleónovité represents a remarkable family of reptiles known for their adaptive coloration, prehensile tails, and distinctive eye movements. These reptiles are celebrated for their ability to blend into diverse habitats, communicate visually, and hunt efficiently. Studying chameleónovité provides valuable insights into evolutionary adaptation, behavioral ecology, and the relationship between organisms and their environment.
These reptiles primarily inhabit tropical forests, savannas, and shrublands, where their unique physical adaptations allow them to navigate complex ecosystems. Chameleónovité serve as a model for understanding species evolution, predator-prey interactions, and environmental adaptation strategies.
Also, explore Guizhou Meigan Technology: Driving Innovation And Digital Transformation
Physical Adaptations and Survival Mechanisms
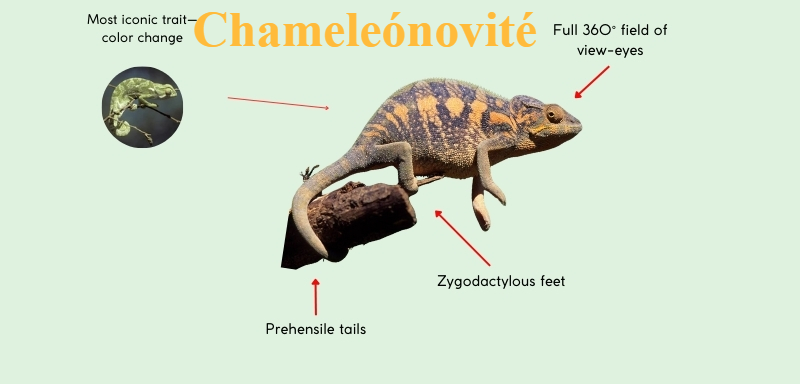
Key Features That Define Chameleónovité
One of the most notable features of chameleónovité is their color-changing ability, which is controlled by specialized skin cells called chromatophores. This adaptation allows them to regulate temperature, camouflage against predators, and communicate with other chameleons. Color changes can indicate mood, territorial behavior, or mating readiness.
Chameleónovité also possess independently moving eyes, allowing nearly 360-degree vision. This enables them to monitor their surroundings effectively while remaining motionless. Additionally, their long, sticky tongues allow for rapid prey capture, making them efficient hunters. These traits collectively enhance survival and demonstrate the intricate evolutionary design of the species.
Habitat, Distribution, and Ecological Role
Where Chameleónovité Thrive
Chameleónovité are found across Africa, Madagascar, and parts of Asia, favoring warm climates with ample vegetation. Dense foliage provides both protection and hunting opportunities, making it an ideal environment for these arboreal reptiles. Their presence contributes to maintaining ecosystem balance by regulating insect populations and serving as prey for larger animals.
These reptiles also act as indicators of environmental health. Changes in chameleónovité populations can reflect alterations in habitat quality, climate conditions, and biodiversity levels. Studying their habitats provides essential data for conservation efforts and ecological research.
Scientific Importance and Applications
Why Chameleónovité Matter in Research
Chame-leónovité offer significant contributions to biological research, particularly in areas like physiology, genetics, and behavioral studies. Their color-changing mechanisms inspire research in biomimicry, adaptive materials, and visual communication systems. Observing their hunting techniques, social behavior, and reproductive strategies provides insights into evolutionary pressures and species survival mechanisms.
Beyond biology, chame-leónovité influence educational and technological applications. Their unique adaptations inspire innovations in camouflage materials, robotic design, and visual signal technology, showcasing the broader impact of understanding these reptiles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chame-leónovité are one of the most fascinating reptile families due to their adaptive traits, ecological roles, and scientific significance. Their color-changing ability, specialized vision, and hunting strategies highlight the complexity of evolutionary adaptations. Studying chame-leónovité enhances our understanding of biodiversity, ecosystem health, and biological innovation. Preserving their habitats ensures continued research opportunities and maintains the ecological balance crucial to sustaining natural environments.
FAQs
- What defines chame-leónovité among reptiles?
Chame-leónovité are known for their color-changing skin, independently moving eyes, and long, sticky tongues for hunting. - Where are chame-leónovité commonly found?
They inhabit tropical forests, savannas, and shrublands in Africa, Madagascar, and parts of Asia. - How do chame-leónovité capture prey?
They use their rapid, extendable tongues to catch insects and small animals efficiently. - Why are chame-leónovité important for ecosystems?
They regulate insect populations and serve as prey, maintaining food chain balance. - How do chame-leónovité inspire scientific research?
Their adaptive features influence studies in physiology, genetics, biomimicry, and innovative technologies.